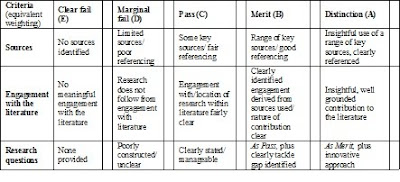
The Methodology section relates to SIX rows of the marking grid as shown below
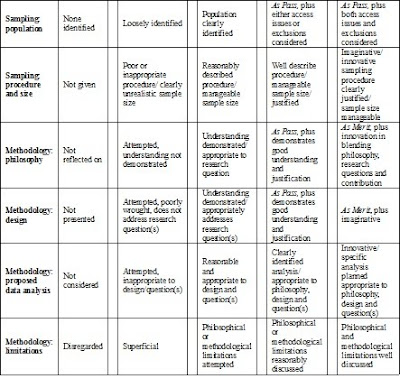
Sampling population – this section identifies the group (or set of things) that you will be making your knowledge claims about, your population. You need to identify this group (who/what are they and why are they interesting), consider issues of access (a realistic outline of how you are going to get to them/it) and why you have excluded other groups (who/what you will not be studying and why).
Sampling procedure and size –You need to explain the procedure you will use or have used to select your sample, the size and makeup of the sample (including a discussion of saturation for qualitative study) and a justification of your choices – why have you chosen to use your sample selection procedure?
Methodology – Philosophy – here you will discuss your particular methodology, and give a justification of why it is appropriate to answer your research question (e.g. phenomenology, causal research)
Methodology – Design – here you explain how you will collect your data, your method (e.g. focus groups, techniques, questionnaire, experiment). Again you must justify your choices, why are they the most useful ones to answer your research question?
Methodology – proposed data analysis – here you explain how you will analyse your data, once collected. This should be appropriate to the methodology, methods chosen and your question.
Methodology – limitations – here you show that you understand the limitations of your proposed research. You need to discuss the limitations of your philosophy and design in order to gain full marks.
The marker will be looking to see that all of these sections make sense when looked at as a whole. For example, if you claim you are doing phenomenology in your philosophy section, then in your design section you outline that you will be using questionnaires for the main part of your data collection and analyzing them using SPSS, you will lose marks as this does not make sense. The marker will be looking at each section as it relates to what has gone before, make sure yours makes sense read as a whole and not just as separate sections!!
7) Project plan
Use a Gannt style of chart to sensibly map out what areas of research you will undertake across the timescale. You should be familiar with Gannt charts from your other study, but if not, you can find information about Gannt charts on the internet.
For more help on Dissertation writing or porposal writing please feel free to contact www.HelpWiththesis.com
GOOD LUCK!!